China, with a population of 1.411 billion and a rapidly evolving education landscape, remains the largest source of international students worldwide. Each year, over 1.02 million Chinese students pursue education abroad, driven by career opportunities, access to world-class universities, and specialized programs not available locally. These students represent a diverse group—some seeking scholarships and research opportunities, while others pursue bachelor’s and postgraduate programs as a pathway to global careers and potential migration. The United Kingdom, United States, Hong Kong, and Canada remain top destinations, attracting Chinese students with their high-ranking institutions, work-study options, and strong employment prospects after graduation. With shifting demographics, increasing digital influence, and changing economic factors, universities worldwide must adapt to new trends in Chinese student recruitment to remain competitive in this dynamic market.
China’s Market for International Education
China’s rapid economic growth has positioned it as a global powerhouse, with key metropolitan cities driving innovation and development. Major hubs like Shanghai, Beijing, Shenzhen, and Guangzhou lead the country’s economy, with Shanghai boasting the highest GDP at 4,721.87 billion yuan in 2023. These cities serve as financial, technological, and educational centers, attracting international students seeking high-quality education and career opportunities.
The rise of emerging economic hubs such as Chengdu, Hangzhou, and Wuhan highlights China’s expanding industrial and academic landscape. These cities offer strong industry connections, government support, and a lower cost of living, making them attractive alternatives for international students.
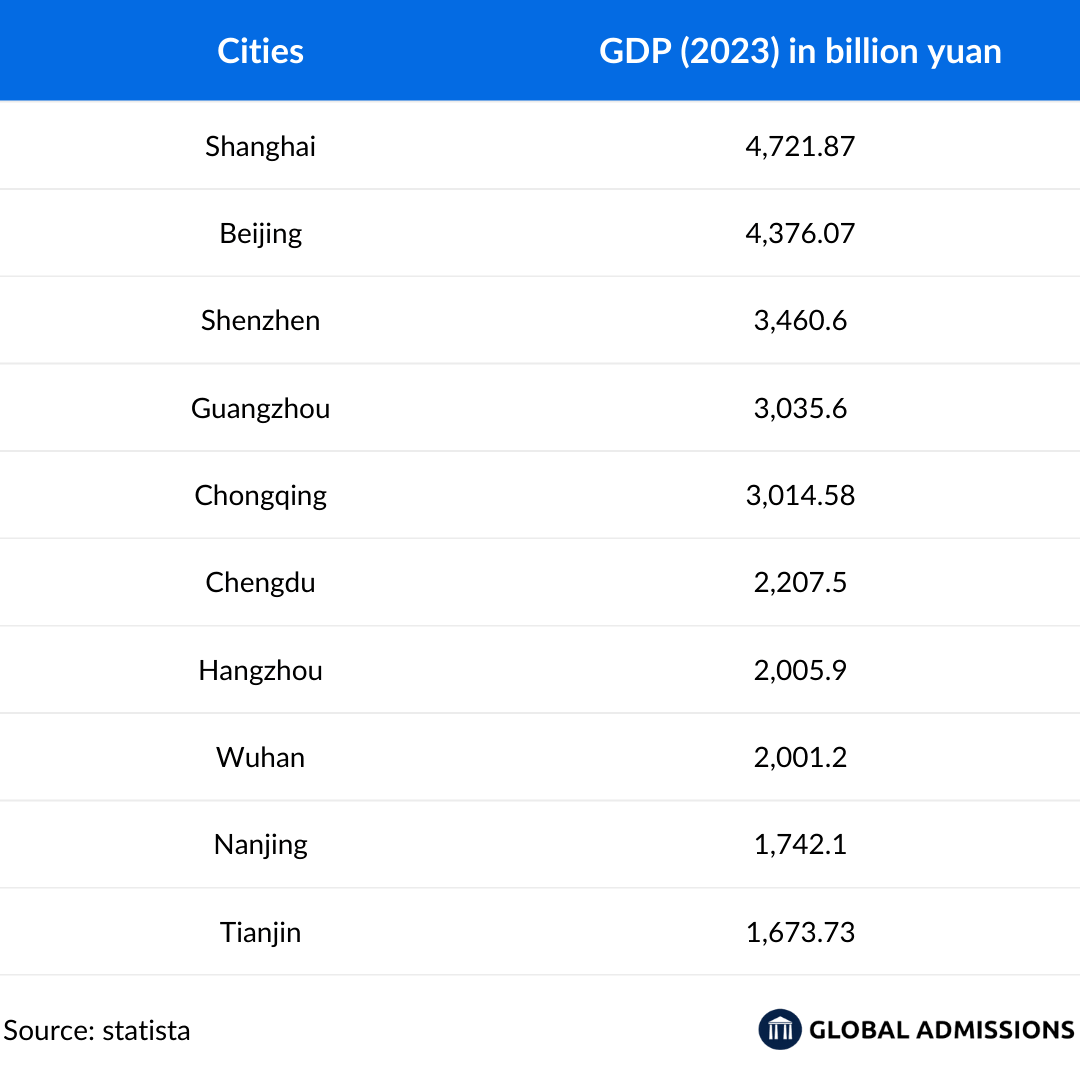
With China’s focus on global collaboration and higher education expansion, these economic hubs represent significant potential markets for international student recruitment.
China Education System
Understanding the education system is essential for universities looking to attract Chinese students. China has the world’s largest education system, with over 270 million students and 15 million teachers. The system is structured into basic, secondary, and higher education, with a strong emphasis on academic excellence and standardized testing.
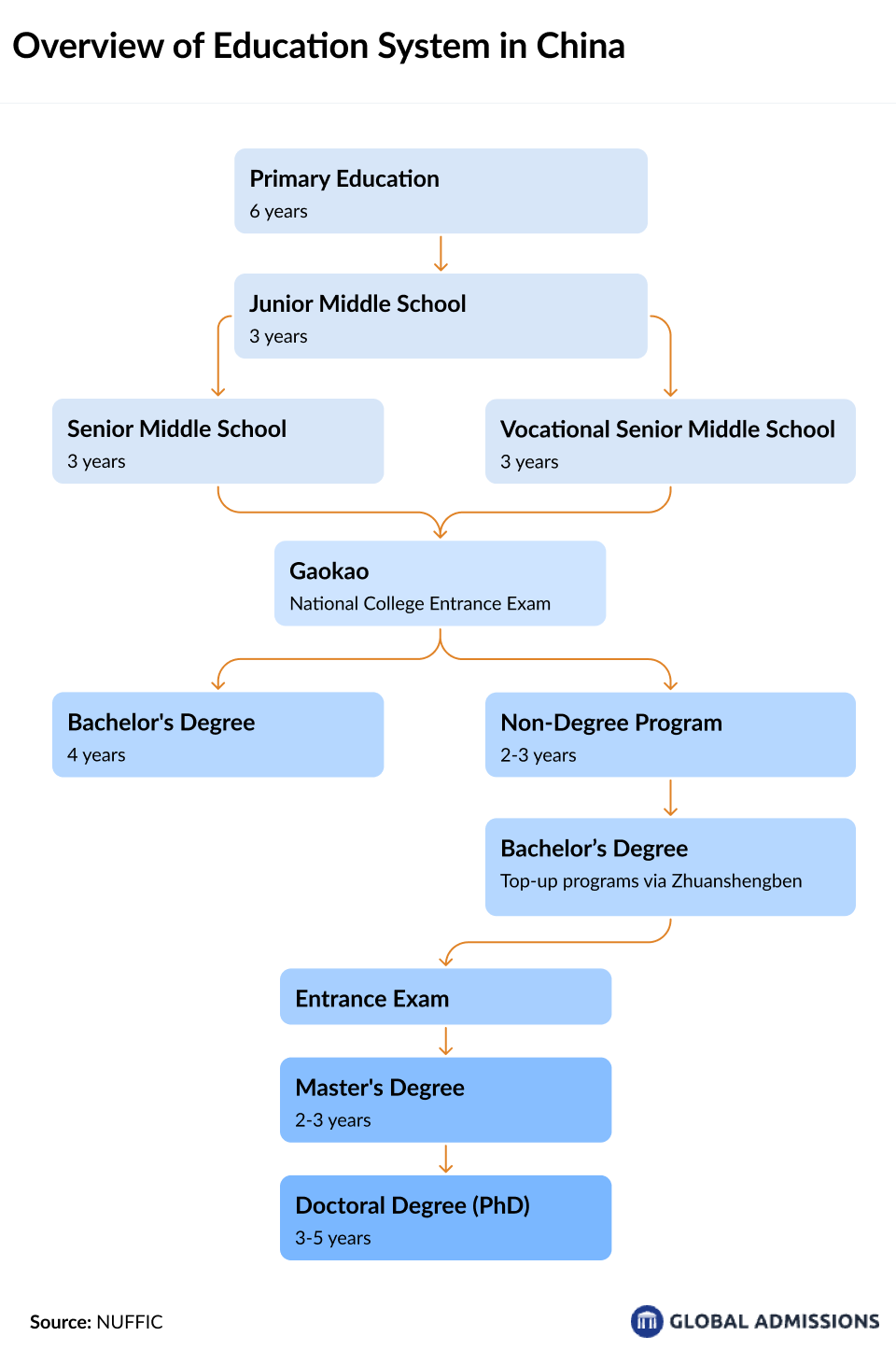
China’s education system is highly competitive, particularly at the university level, where students must pass the Gaokao to gain entry into top institutions. Vocational education is also expanding, providing alternative pathways for students interested in practical, career-focused training.
With investment in education consistently above 4% of GDP, the country continues to enhance both academic and vocational training programs, including fields like robotics, AI, and renewable energy. The demand for international education remains strong, driven by students seeking diverse experiences, globally recognized degrees, and career opportunities abroad.
China's International Student Market
China continues to be one of the largest sources of international students, with a strong demand for overseas education driven by career aspirations, academic prestige, and global opportunities. The decision-making process for studying abroad is highly influenced by parents, who play a crucial role in financing education and selecting institutions based on factors such as reputation, career prospects, and financial investment. While students prioritize academic programs, employment pathways, and cultural experiences, parents often focus on long-term stability and return on investment.
In the digital age, social media and search engines are the primary research tools for both students and parents. Given China’s unique internet ecosystem, platforms like WeChat (87.3%), Douyin (78.4%), and Xiaohongshu (51.2%) are widely used for gathering information and engaging with universities. Xiaohongshu, in particular, has become a key platform for students to seek peer advice, read alumni experiences, and explore study options. Since Google is restricted in China, students rely less on traditional search engines like Xiaohongshu and more on social platforms for authentic, user-generated content when researching study abroad opportunities.
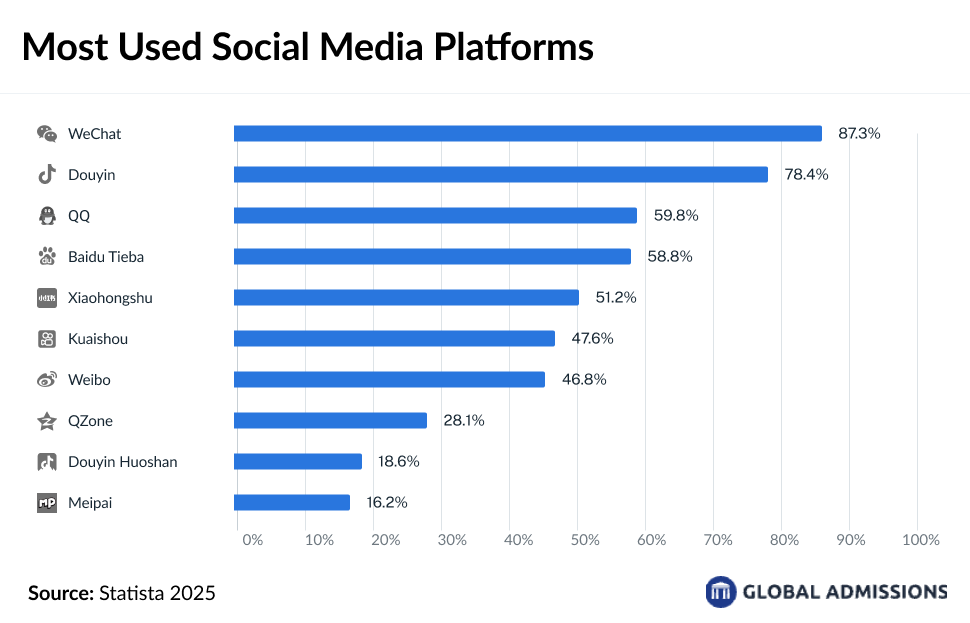
As 74% to 86% of Chinese students rely on education agents, parents also engage with these intermediaries to ensure their children choose the best-fit institutions. Universities aiming to attract Chinese students should focus on building strong digital presences on social platforms, leveraging peer recommendations, and ensuring visibility on Xiaohongshu to effectively reach both students and their decision-making families.
Top Study Destinations of Chinese Students
China remains one of the largest sources of international students worldwide, with an increasing number seeking education abroad for better career prospects, quality education, and global exposure. The United Kingdom (41%) is the top destination, followed by the United States (30%), Hong Kong (19%), Canada (15%), Japan (14%), Singapore (14%), and Australia (12%). Other destinations, including Germany (10%), France (6%), and New Zealand (5%), are also attracting Chinese students, particularly for specialized programs and lower tuition costs.
While the UK and US remain dominant, there has been a shift in preferences due to rising tuition fees, stricter visa policies, and increasing opportunities in Asia. Destinations like Japan, Malaysia, Taiwan, and South Korea have intensified their international recruitment efforts, offering competitive scholarships, post-graduate employment options, and lower living costs, making them attractive alternatives. Additionally, many Chinese students are now prioritizing destinations that provide strong career pathways, internship opportunities, and favorable immigration policies.
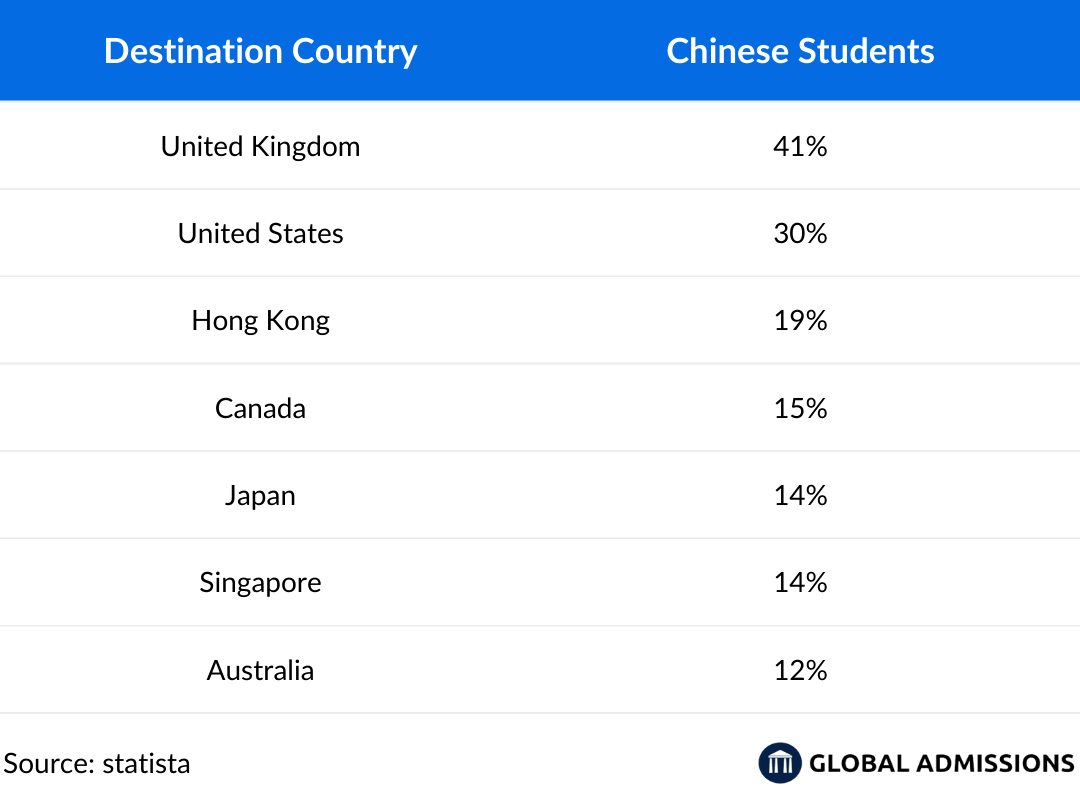
Economic factors also play a role in shaping mobility trends. The cost of studying abroad is a significant consideration, and some students are now exploring more affordable destinations within Asia instead of the traditionally favored Western countries. With government policies continuously evolving, universities looking to recruit Chinese students need to adapt by emphasizing affordability, career support, and digital engagement strategies to remain competitive in this dynamic market.
Challenges Chinese Students Face
Chinese students pursuing education abroad encounter several challenges that impact their academic and personal experiences. Language barriers remain a significant hurdle, as many struggle with academic writing, classroom discussions, and social interactions despite years of prior study. This, in turn, affects their confidence and ability to integrate into the local community. Additionally, cultural differences present difficulties, particularly in adapting from a collectivist society to an individualistic culture where self-expression and independent decision-making are emphasized.
Homesickness and social isolation are common concerns, as students are often far from family support systems, making it difficult to build new social networks. High academic expectations, both from family and personal aspirations, add further stress, particularly as they adjust to different teaching styles and assessment methods. Financial pressures, including tuition fees, living expenses, and unforeseen costs, also create burdens, especially for those who seek part-time work to offset expenses.
Navigating visa regulations and work permits can be complex, adding to students' anxieties about legal requirements and future career opportunities. A lack of reliable information about applications, accommodation, and job prospects further complicates their journey, with some students expressing skepticism towards agents and online resources due to concerns over misinformation or fraud. Addressing these challenges through comprehensive student support, accessible resources, and culturally sensitive guidance is essential in ensuring a smooth transition and successful international study experience.
Cultural Influences on Chinese Students’ Study Abroad Decisions
Chinese students often experience a unique transition when moving from a collectivist society to an individualistic culture while studying abroad. In China, education decisions are heavily influenced by family, agents, and peer recommendations. This makes it essential for universities to understand the social and cultural dynamics that shape their choices. Many students rely on external validation when making decisions, and adapting to an environment where independence and self-reliance are expected can be challenging. Universities that provide structured support, mentorship programs, and clear guidance during the arrival period can help ease this adjustment and ensure student success.
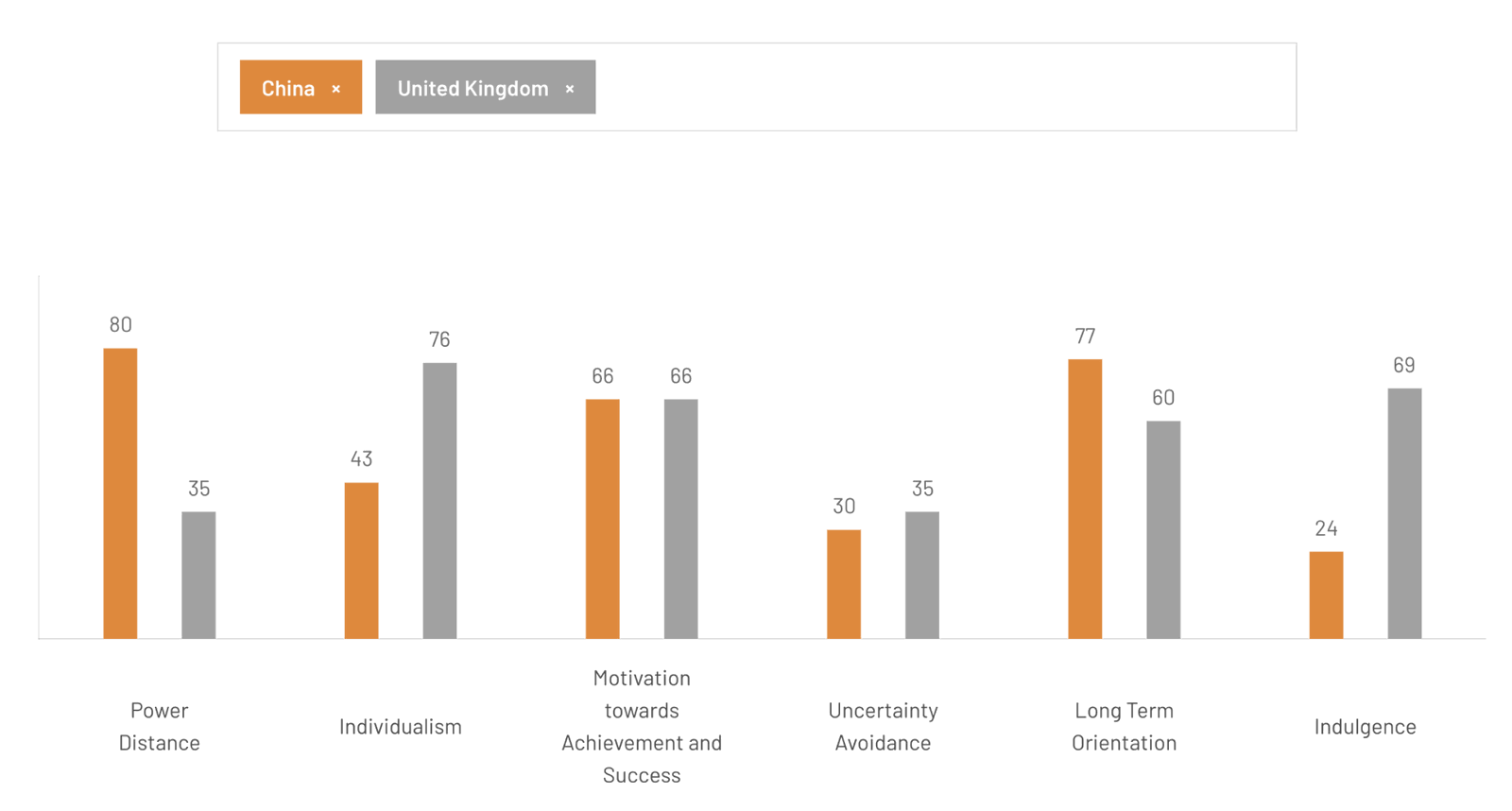
Parents play an important role in funding their children’s overseas education, often saving for years to ensure access to quality institutions. In many cases, students follow their parents’ preferred destinations, with choices driven by university prestige, career opportunities, and financial investment returns. As a result, universities looking to attract Chinese students must build trust with families, offer clear career pathways, and ensure strong post-graduation employment support. Given that 74% to 86% of Chinese students use education agents, universities must also consider the role of intermediaries in shaping student decisions.
Millennials fueled the study-abroad boom, prioritizing global experiences for career advancement. Gen Z (Zoomers) are more pragmatic and career-driven, focusing on the return on investment in education, employment pathways, and digital learning experiences. The Alpha generation, which is smaller due to China’s declining birth rates, is highly tech-savvy and AI-driven, likely favoring hybrid learning models and flexible international education options. With fewer students in younger generations, global institutions must adapt to a smaller but highly digital-first market, using personalized recruitment strategies, tech-driven learning formats, and career-focused education pathways to remain competitive.
A Broader Global Perspective
Understanding the evolving landscape of Chinese international student mobility is crucial for universities seeking to attract and support this diverse student population. As Chinese students navigate challenges such as cultural transitions, language barriers, and financial considerations, universities that provide comprehensive student support, clear communication, and strong peer networks will have a competitive advantage.
The role of parents, digital platforms, and education agents in shaping students’ decisions cannot be overlooked. Universities that invest in localized digital marketing strategies, engage in peer-to-peer recruitment, and build trust through transparent information and services will be better positioned to capture this market.
Also, shifting generational preferences indicate that younger students are becoming more open to regional destinations and alternative education pathways. Universities that recognize these changing trends and offer flexible study options, hybrid learning, and career-oriented programs will appeal to the next wave of outbound Chinese students.
Ultimately, fostering a student-centered approach—one that prioritizes accessibility, inclusion, and long-term career outcomes, will not only benefit individual students but also enhance global collaboration and cross-cultural exchange. As the demand for international education continues to evolve, universities that embrace these strategies will build stronger academic networks and long-term relationships with Chinese students, ensuring sustained growth and global engagement.
Attract and Engage a Diverse International Student Body
Attracting a diverse body of international students is essential for building a globally connected and dynamic university community. Global Admissions helps universities connect with highly motivated students from over 195 countries, offering strategic marketing solutions, digital engagement, and insights-driven recruitment strategies.
Our platform is designed to streamline your recruitment process, enhance visibility, and match your programs with students actively seeking opportunities abroad. With over 200,000 registered students and 1 million+ annual searches, we provide targeted campaigns to help your institution reach the right audience.

Download the 2025 China International Student Market & Trends Report to gain deeper insights into student mobility, decision-making factors, and strategies to effectively engage with Chinese students.
Read More:
International Student Recruitment Market in the Philippines
The Role of Community in International Student Recruitment

