As the world grows to be more interconnected, an increasing number of students are choosing to study at universities abroad. While it’s an exciting opportunity to experience life in a completely new country, it’s also natural to have concerns about adapting to a new environment and navigating cultural differences.
One of the biggest challenges that international students are often faced with is the large differences between Eastern and Western cultures. Whether you’re an international student studying in the West for the first time or vice versa, understanding the local culture will help you successfully adapt to a new environment, build stronger connections with others, communicate more effectively, and see things from different perspectives.
This article will explore some of the key cultural differences between Eastern and Western cultures that are important to consider when studying abroad.

Where Are Eastern & Western Countries?
Defining Eastern and Western cultures can be a complex task, as there are many cultural differences and nuances within each category, and all cultures evolve over time.
Generally speaking, Eastern cultures are associated with the countries of Asia, including China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam, among others. These cultures often place a strong emphasis on tradition, family values, and respect for authority. Western cultures, on the other hand, are associated with countries in Europe and the Americas, including the United States, Canada, and much of Europe. These cultures are often characterized by individualism, a focus on personal freedoms, and a tendency towards innovation and progress.
1) Communication Styles
Eastern Cultures |
Western Cultures |
| Indirect communication is considered to be more polite and respectful.
Meanings are conveyed subtly and indrectly through the use of nonverbal cues such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language. Politeness and formality are important in social interactions. This includes the concept of saving face, maintaining harmony and showing regard for authority. ★ Tip: Listen carefully to understand the subtle nuances and underlying messages being communicated. The non-verbal cues can help you better understand the context of conversations. |
Direct communication is preferred (in contrast, this can be perceived as blunt or even rude in Asian cultures!).
Meanings are clear and concise. Communication styles emphasize assertiveness, individuality, and critical thinking. Politeness is important, but not necessarily in formal or hierarchical settings. ★ Tip: Express your thoughts and opinions clearly and confidently, even if it may be uncomfortable at first. Practice active listening, asking questions to clarify understanding, and providing feedback to show that you are engaged in the conversation. |

2) Relationships & Individuality
Eastern Cultures |
Western Cultures |
| Collectivism is prioritized over individualism, with a focus on group harmony and interdependence.
Groups are considered more important than the individual. Family and community ties are highly valued. Hierarchical structures are common in social and professional settings.It is important to have respect for elders and authority figures. ★ Tip: It is common to seek consensus and consult with others when making decisions. Embrace the support you receive and help others out in return. |
Individualism and personal freedoms are highly valued.
People are expected to be independent and self-sufficient. They are encouraged to express their unique qualities and pursue their own goals. There is less emphasis on hierarchical structures. People are expected to be treated fairly regardless of their social status or background. ★ Tip: If you grew up in Asia, you might find that pursuing your own goals can be both iberating and challenging. Don’t be afraid to focus on your individual achievements while maintaining a balance with your own culture. |

3) Time Orientation
Eastern Cultures |
Western Cultures |
| Time is often viewed as cyclical and flexible, with less emphasis on punctuality and strict schedules.
It may not be considered a major issue if you arrive late for a lecture or class (though we don’t recommend it, you may miss out on something important!). Relationships and personal interactions are often prioritized over punctuality. There is more emphasis placed on the present moment. |
Time is viewed as a commodity that can be used, spent, or wasted.
Students are expected to be punctual and adhere to their schedules. This means arriving to your lecture on time, or even ten minutes earlier to seat yourself and prepare. Being late can be seen as disrespectful or inconsiderate. |
★Tip: Eastern and Western cultures have different attitudes towards the value of time, which can sometimes lead to misunderstandings and miscommunications. As an international student, you may need to adjust your expectations and behavior in relation to time.

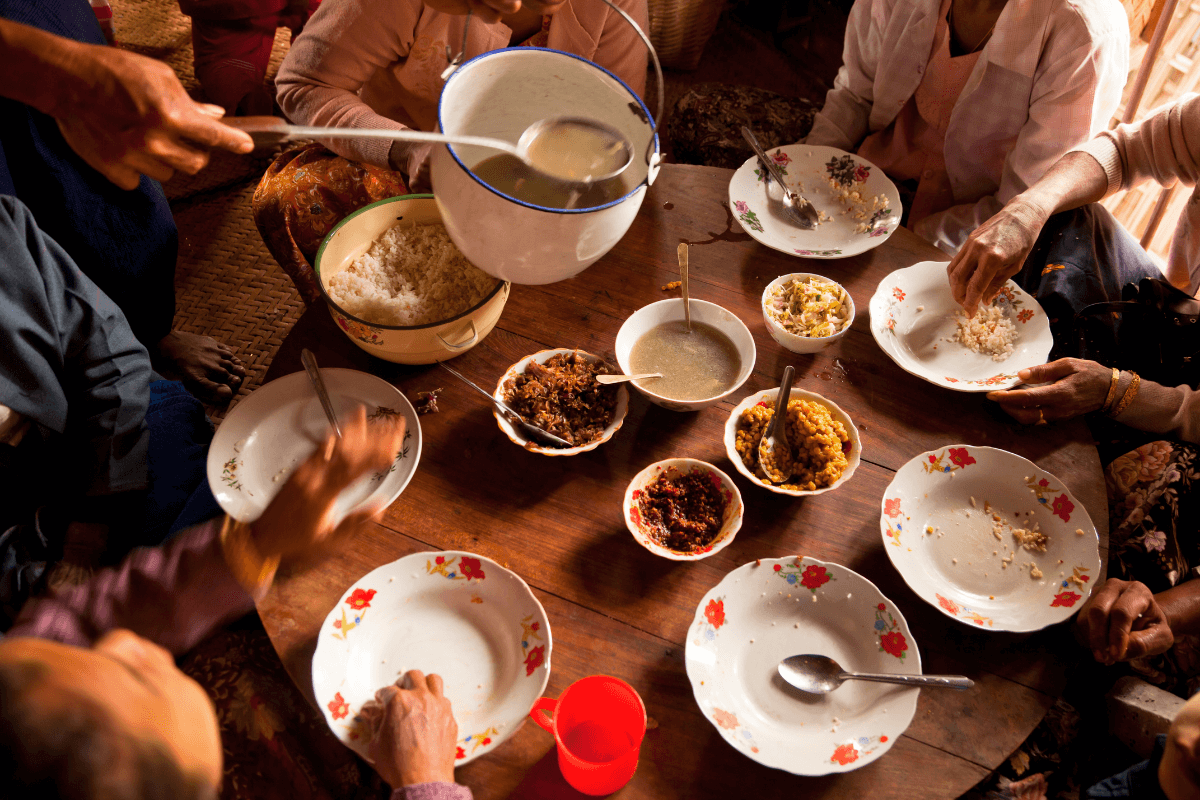
4) Dining & Cuisine
Eastern Cultures |
Western Cultures |
| Meals are often shared and enjoyed communally. Dishes are usually laid out on the center of the table for everyone to serve themselves.
The food is focused on the balance and harmony of flavors, with a preference for fresh ingredients. Asian countries often eat rice as a staple food, as well as noodles, tofu, and a variety of vegetables and spices. You may see chopsticks more frequently, and knives more rarely. Some cultures, such as in India, prefer to eat with their hands. ★ Tip: It is sometimes common to offer food or drink to others before serving oneself. |
Meals are served in individual portions and plated separately.
The food is usually selected based on personal choice and convenience. Western cuisine usually centers around meat potatoes, bread, and dairy products, with less emphasis on rice and noodles.There is a greater prevalence for fast food and processed foods. Typical utensils such as knives, forks, and spoons are used. ★ Tip: In some Western cultures, such as France, it is considered impolite to start eating before everyone has been served. |

The Importance of Experiencing New Cultures
Learning about different customs, traditions, and values gives university students the opportunity to broaden their perspective and gain a deeper understanding of the world around them. You can develop a more nuanced appreciation of cultural diversity and become more open-minded and accepting of others.
You may need to learn a new language or adjust to different social norms which can be challenging… but ultimately, just as rewarding. By stepping outside your comfort zone and navigating unfamiliar situations, you can develop resilience and confidence, as well as valuable skills such as adaptability, communication, and problem-solving.
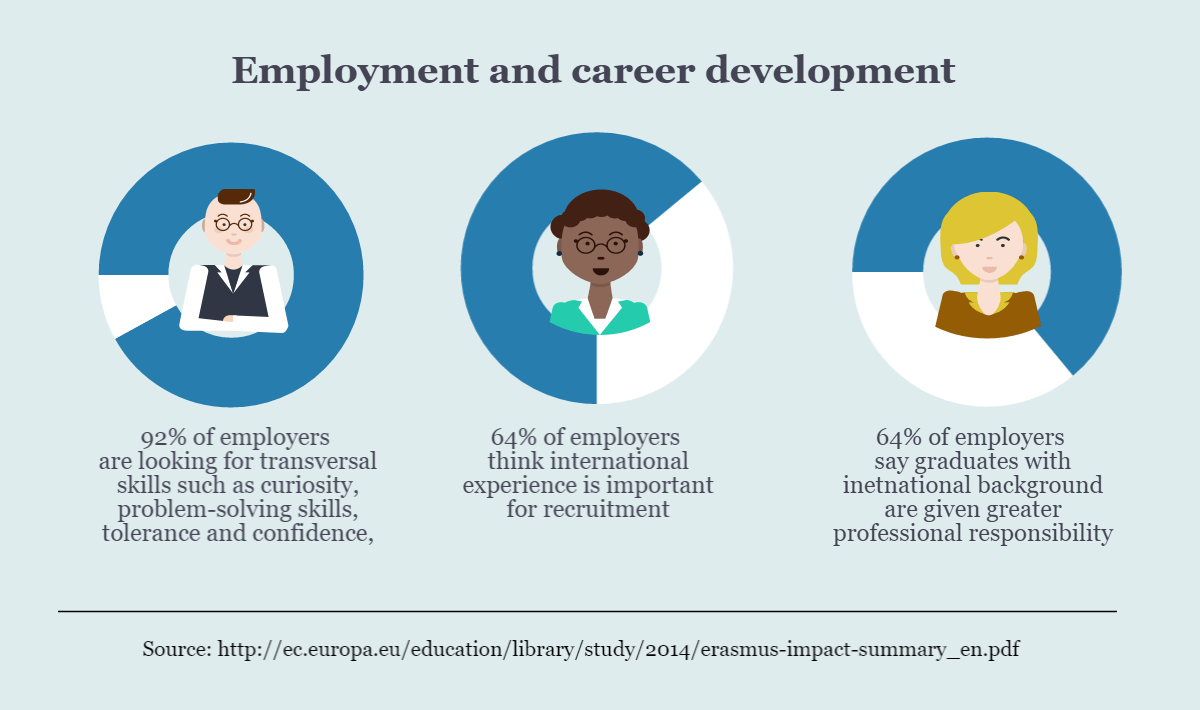
By studying abroad, you will gain a significant asset for your future career. Many employers value candidates who have cross-cultural competency and can work effectively with people from different backgrounds. By demonstrating your time at university studying in a diverse environment in your resume, you will have an advantage over competing job candidates and increase your chances of success in a wide range of industries.
The Key to a Successful University Experience
As an international student, understanding and respecting cultural differences is vital to a positive university experience. From communication styles and perception of time to food etiquette and respect for hierarchy, you can see that Eastern and Western cultures vary in many ways. By learning and respecting these differences, it gets easier to step out of your comfort zone and apply to universities abroad. Embrace the opportunity to immerse yourself in a new culture, meet new people, and gain a unique perspective that will benefit you for years to come.
At Global Admissions, we make it easy for students to find and apply to universities abroad. Find out how we can help.

